Chrome and Firefox Security Updates
October 21, 2024
Roundcube Webmail Vulnerability Exploited by Hackers
October 21, 2024The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing the digital landscape, connecting millions of devices across the globe. From smart homes to industrial machinery, IoT devices are enhancing efficiency, convenience, and innovation. But as IoT becomes increasingly integrated into our daily lives, its impact on cyber security cannot be ignored. The convergence of these connected devices introduces new vulnerabilities, posing both opportunities and challenges for securing digital environments.
The Rapid Growth of IoT and Its Impact on Security
IoT devices have exploded in popularity, from smart thermostats to wearable tech, to the industrial systems that power cities and businesses. This massive growth brings with it an unparalleled volume of data, and while IoT opens doors to technological advancements, it also creates potential attack vectors for cyber criminals.
With every device added to a network, the potential for cyber threats expands. Each connected device is a gateway to sensitive data, making IoT ecosystems prime targets for hackers. Unlike traditional computing devices, many IoT gadgets lack robust security features, providing a fertile ground for cyber attacks such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), ransomware, and data breaches.
Vulnerabilities in IoT Devices: A Cyber Criminal’s Playground
The very nature of IoT devices makes them vulnerable to cyber threats. Many of these devices are designed for convenience and efficiency rather than security. Manufacturers often prioritize quick product release over comprehensive security measures, leaving devices open to attacks. IoT devices may come with weak or default passwords, outdated firmware, or limited encryption protocols, all of which provide an easy entry point for cyber criminals.
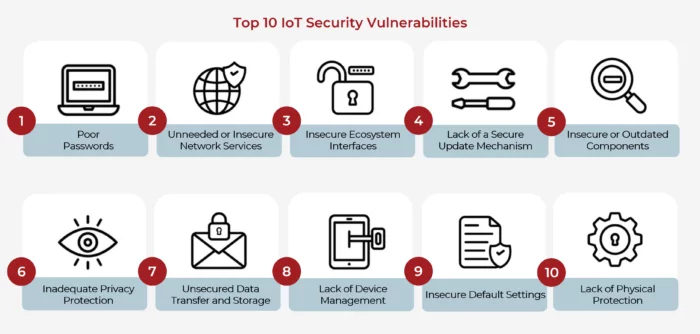
In a cyber security context, every smart device connected to a network acts as a potential weak link. Hackers can exploit these weaknesses to gain unauthorized access to networks, extract data, or use compromised devices in larger cyber attacks, such as botnets.
The Role of IoT in Amplifying Cyber Threats
The scale and diversity of IoT devices amplify the complexity of managing cyber security. Unlike traditional networks, which primarily involve computers and servers, IoT networks may include everything from cameras and refrigerators to industrial sensors and medical devices. These devices often operate autonomously, interacting with one another without human intervention, making it difficult to monitor their security in real-time.
For organizations, the influx of IoT devices means an increased attack surface. The more devices in a network, the more pathways cyber attackers can exploit. IoT devices are also often dispersed across multiple locations, further complicating security management. An unsecured smart meter in a home could provide access to an entire utility network, showcasing how IoT blurs the line between personal and corporate cyber security risks.
IoT and Cyber Security Solutions: A New Frontier of Protection
To mitigate the risks posed by IoT, security experts are developing advanced strategies that protect IoT ecosystems. AI-powered cyber security solutions can monitor and analyze the behavior of IoT devices, flagging suspicious activity before it leads to a breach. Blockchain technology is also being explored to provide decentralized, tamper-proof security layers for IoT networks, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring data integrity.
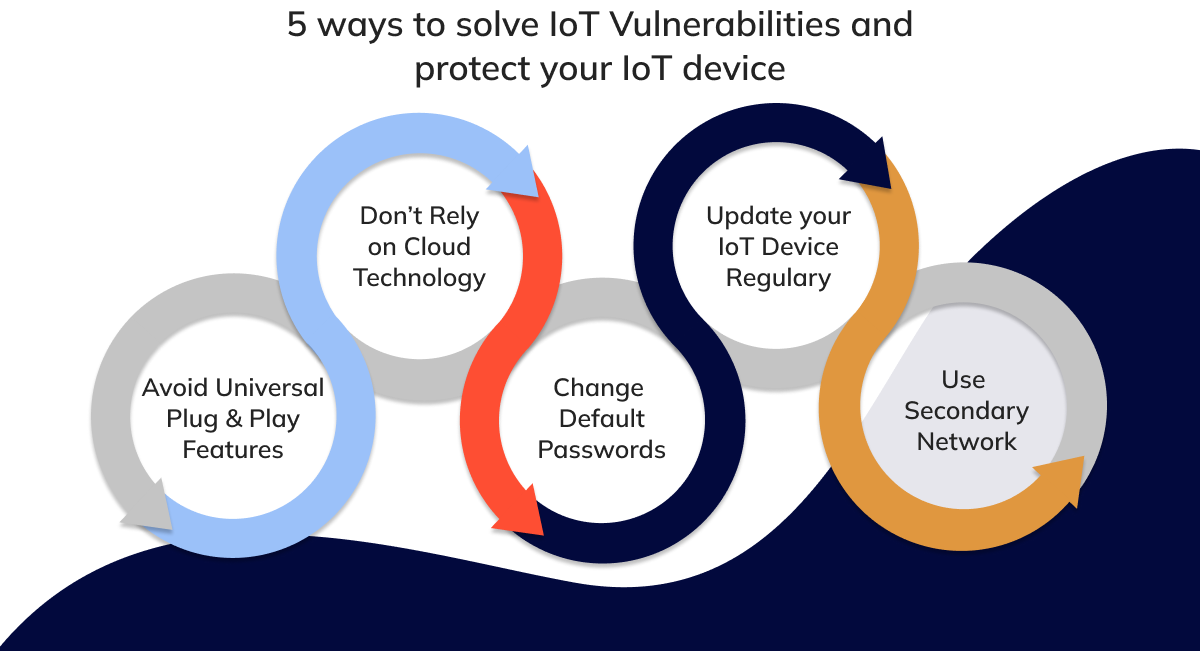
Additionally, regulatory frameworks are emerging to address IoT security standards. Governments and industry bodies are working to ensure that IoT devices meet certain security requirements, such as encryption, patching capabilities, and strong password protocols. The focus is shifting toward embedding security features into IoT devices from the outset, rather than as an afterthought.