Data Breaches in Cybersecurity: A Growing Concern
October 16, 2024
Iran’s Cyber Offensive: Exploiting Windows Kernel Vulnerability
October 16, 2024North Korean cybercriminals have been detected using a Linux-based version of the FASTCash malware to conduct ATM heists by targeting payment switch systems involved in card transactions. This malware enables unauthorized cash withdrawals from ATMs by infecting network systems that manage card payments, explained a security researcher known as HaxRob.
Originally identified by U.S. authorities in October 2018, FASTCash has been linked to North Korean groups targeting financial institutions in Africa and Asia since late 2016. The malware compromises bank servers that control payment switches, allowing attackers to execute fraudulent transactions. Notable incidents include simultaneous withdrawals from ATMs across over 30 countries in 2017 and from 23 countries in 2018.
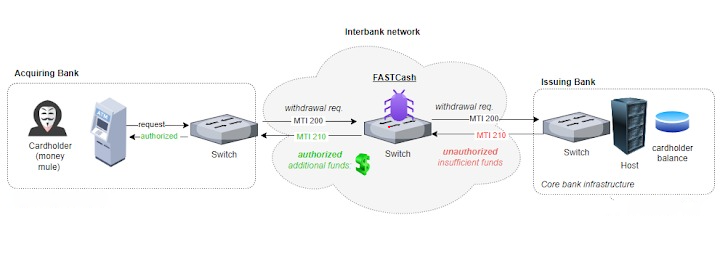
While earlier versions of the malware targeted Microsoft Windows and IBM AIX systems, recent findings reveal that Linux variants designed to attack Ubuntu Linux 20.04 systems appeared on the VirusTotal platform in mid-June 2023. This new variant, a shared object file named “libMyFc.so”, intercepts and alters ISO 8583 messaging—used in debit and credit card processing—to approve transactions normally declined due to insufficient funds. By altering these messages, the malware authorizes withdrawals of random amounts in Turkish Lira, ranging from 12,000 to 30,000 Lira (approximately $350 to $875).
The discovery of this Linux version highlights the ongoing threat and the importance of enhancing detection capabilities in Linux server environments, which are often inadequate, according to the researcher.