FIDO’s latest proposal facilitates safe Passkey Migration between Platforms
October 16, 2024
New FASTCash Linux Malware Hits ATM Payment Switches
October 16, 2024In today’s digital age, data breaches have become one of the most significant cybersecurity threats facing organizations and individuals alike. A data breach occurs when sensitive, protected, or confidential information is accessed, disclosed, or stolen by unauthorized individuals or entities. This can include personal data like social security numbers, financial information, health records, and corporate secrets. As businesses and individuals increasingly rely on digital platforms, the risks associated with data breaches continue to escalate.
One of the main reasons data breaches are so prevalent is the evolving sophistication of cyberattacks. Hackers employ a variety of techniques to exploit vulnerabilities in software, hardware, or human error. Phishing, ransomware, malware, and social engineering attacks are some common methods used to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. Once cybercriminals infiltrate a system, they can steal, sell, or exploit data for financial gain, espionage, or other malicious purposes.
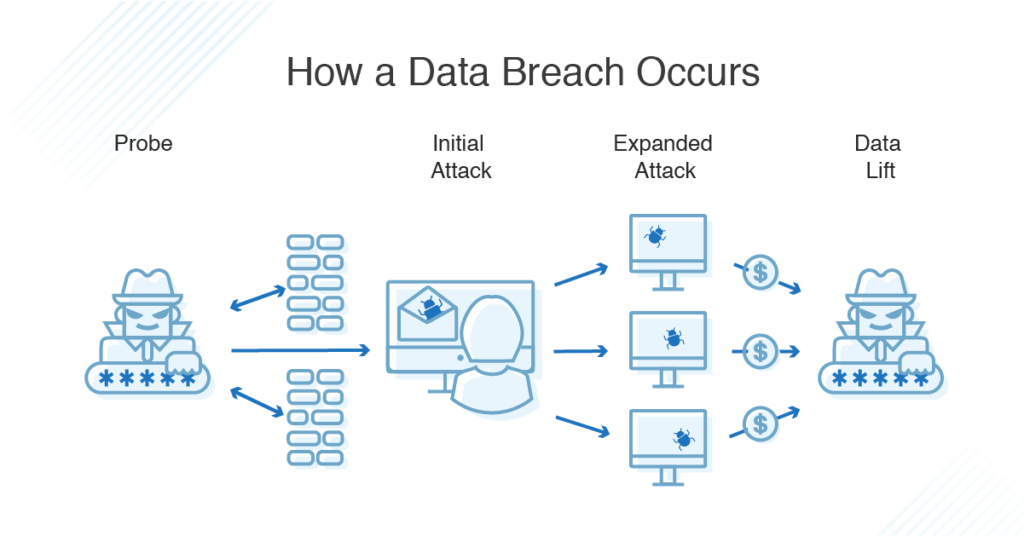
Data breaches can occur across various industries, including healthcare, finance, retail, and government. For instance, the healthcare sector is a frequent target due to the value of medical records on the black market. Similarly, financial institutions are prime targets because of the wealth of personal and financial data they store. Even small businesses, which often have less sophisticated cybersecurity measures, are vulnerable to breaches.
The impact of a data breach can be devastating for an organization. Financial losses, legal penalties, and reputational damage are some of the immediate consequences. According to studies, the average cost of a data breach globally in 2023 was over $4 million. This includes direct costs such as fines and legal fees, as well as indirect costs like loss of customer trust and business disruption. For many organizations, especially smaller ones, a major data breach can be catastrophic.
Moreover, individuals affected by data breaches are at risk of identity theft, financial loss, and privacy violations. Once personal information is exposed, it can be used to commit fraud or other crimes. Victims often face the long-term consequences of repairing their credit, recovering stolen funds, and protecting their identity from further misuse.
One of the primary challenges in preventing data breaches is the rapid pace of technological advancements. As new technologies emerge, they introduce new vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit. Organizations need to continuously update their cybersecurity strategies, adopt best practices, and invest in robust defenses to stay ahead of these threats.