VMware Issues Updated Patch for vCenter Server to Address Critical RCE Flaw
October 23, 2024
How to Secure Your MacOS X Operating System Against Unauthorized Access
October 30, 2024In an era where digital threats are increasing rapidly, cybersecurity has become a critical concern for individuals, businesses, and governments. Traditional security measures often struggle to keep pace with evolving threats such as ransomware, phishing, data breaches, and hacking. Blockchain technology is emerging as a potential solution to many of these cybersecurity challenges, offering enhanced protection, transparency, and integrity in a digital world that is increasingly under attack.
Blockchain’s Immutable Nature
One of the primary advantages of blockchain in cybersecurity is its immutable nature. A blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring that no single entity can alter the information. Once data is entered into the blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to modify or delete it without consensus from the majority of the network. This tamper-resistant property makes blockchain an attractive option for securing sensitive information such as financial records, identity details, and transaction histories.
By decentralizing data storage, blockchain reduces the risk of a single point of failure. In traditional systems, hackers often target centralized databases where all the critical information is stored. Once they gain access, they can manipulate or steal data. However, with blockchain, the data is distributed across a vast network of nodes, making it significantly harder for malicious actors to compromise the system. Any changes to the blockchain must be verified by multiple participants, ensuring a more secure and trustworthy network.
Enhanced Data Integrity
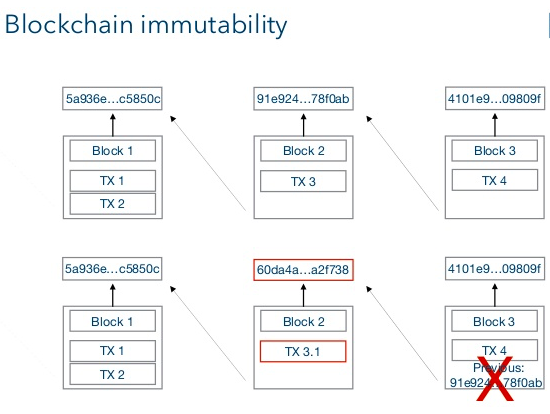
Data integrity is another crucial aspect of cybersecurity that blockchain addresses effectively. In the current digital landscape, verifying the authenticity of data is often a challenge. Blockchain’s cryptographic principles ensure that data cannot be altered once it is recorded. Each block in the chain contains a hash value—a unique fingerprint generated based on the block’s data and the hash of the previous block. If any information is tampered with, the hash changes, signaling an integrity breach across the chain. This capability is particularly beneficial for industries such as healthcare, where the protection of sensitive personal information is paramount.

Decentralized Identity Management
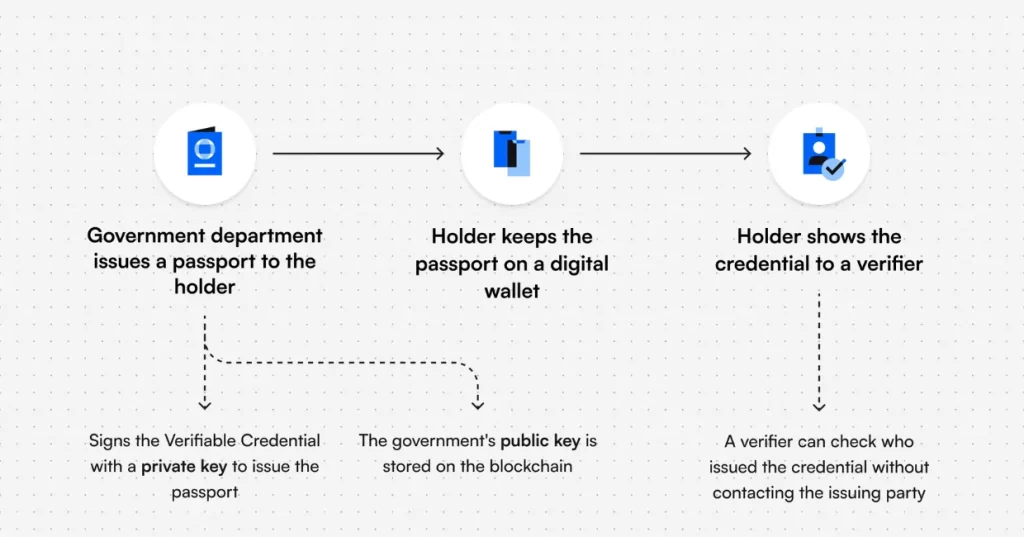
Another significant contribution of blockchain to cybersecurity is its potential for decentralized identity management. Traditional identity verification methods often rely on centralized systems that store personal credentials, which are prone to attacks. Blockchain enables users to create a decentralized, verifiable identity system. Individuals can store their personal data on the blockchain and share it selectively with different entities without exposing all their information to a centralized authority.
This decentralized approach minimizes the risk of identity theft, as there is no single repository for hackers to target. Blockchain also enables the use of self-sovereign identity (SSI), where users have full control over their digital identity and can decide what information to share and with whom.
Securing IoT Networks
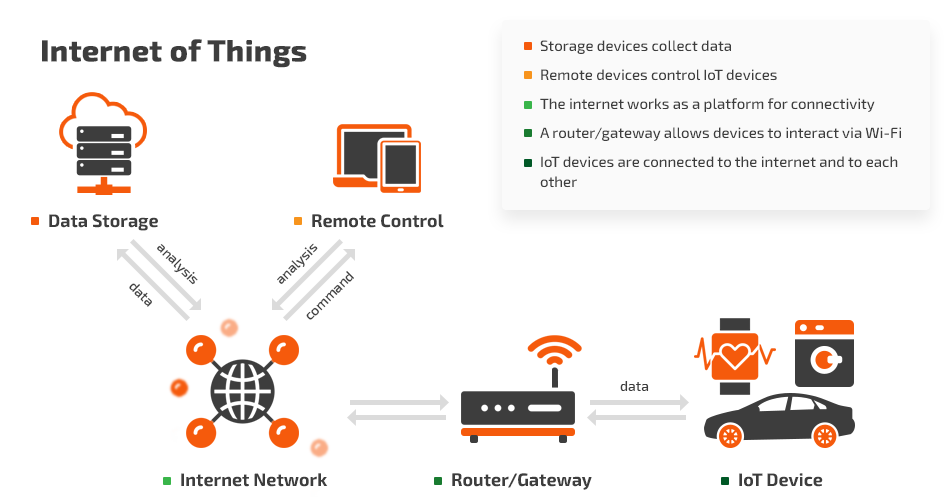
With the rapid expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT), securing the vast network of connected devices has become a growing challenge. IoT devices often have limited processing power and lack robust security features, making them easy targets for cyberattacks. Blockchain can be integrated into IoT networks to enhance security by creating a decentralized and secure communication protocol. Each device on the network can be authenticated and verified through blockchain, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.