Iranian Cyber Group Targets 2024 Olympics
November 2, 2024
What Are the 7 Layers of Cybersecurity?
November 5, 2024In today’s digital era, cloud storage has become an essential tool for individuals and organizations to securely store, access, and manage data. While the cloud offers immense convenience, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, concerns about data security linger. With cyber threats on the rise, it’s natural to wonder: is cloud storage really safe? Let’s delve into how cloud storage stands up from a cybersecurity perspective.
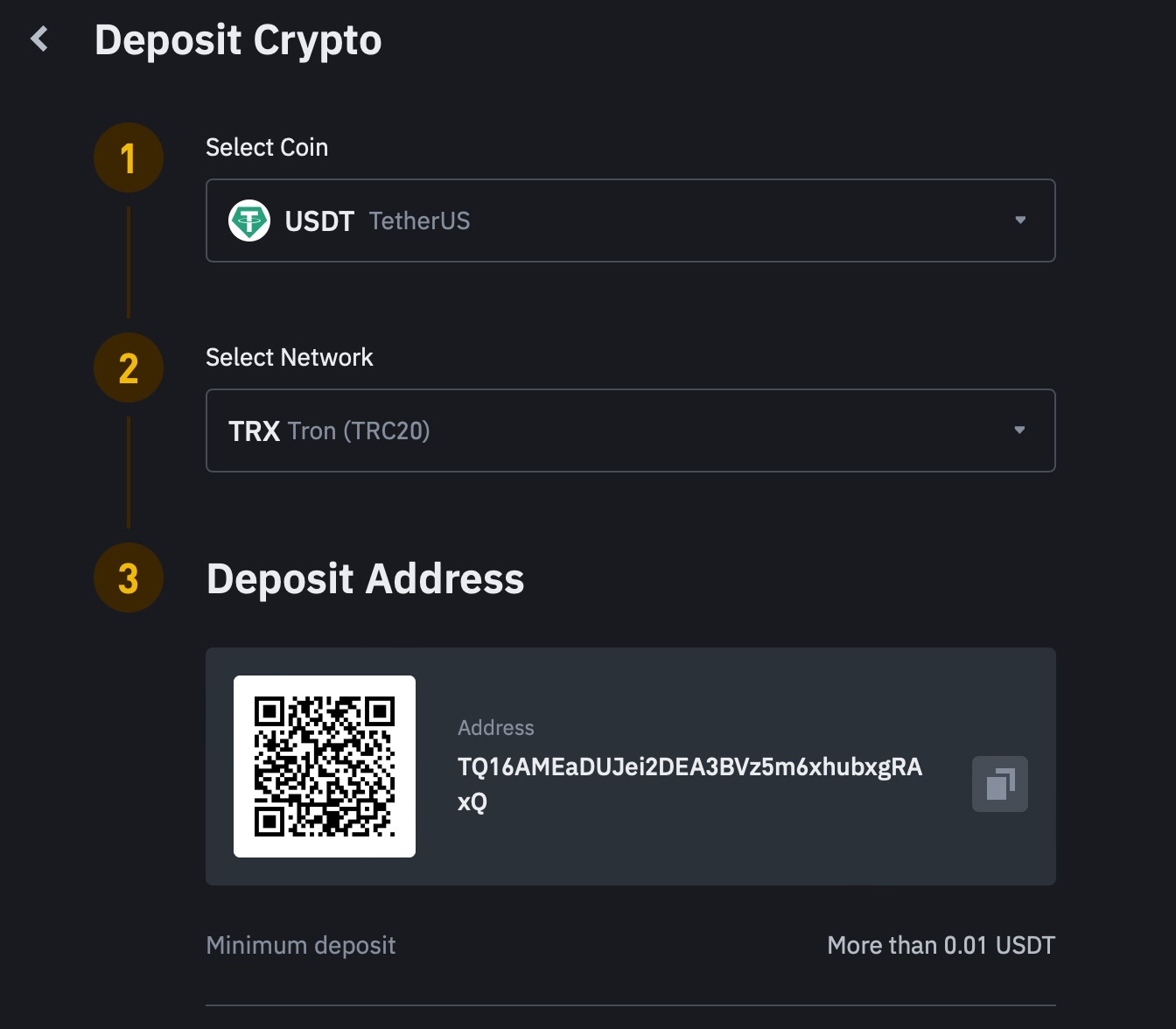
1. Understanding Cloud Storage Security
Cloud storage involves storing data on remote servers managed by a third-party provider. This data can be accessed over the internet from anywhere, making it a flexible solution. However, this accessibility also means data can potentially be exposed to cyber threats if not properly secured. To address these concerns, reputable cloud providers invest heavily in security technologies and best practices to keep data safe from unauthorized access, theft, and data loss.
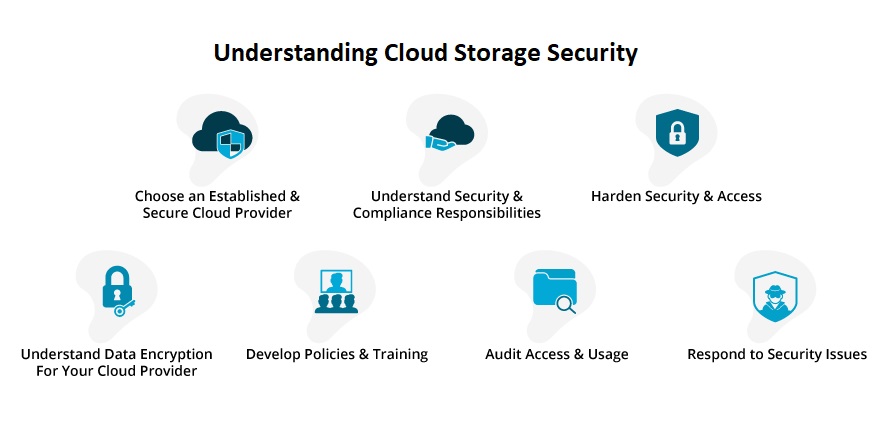
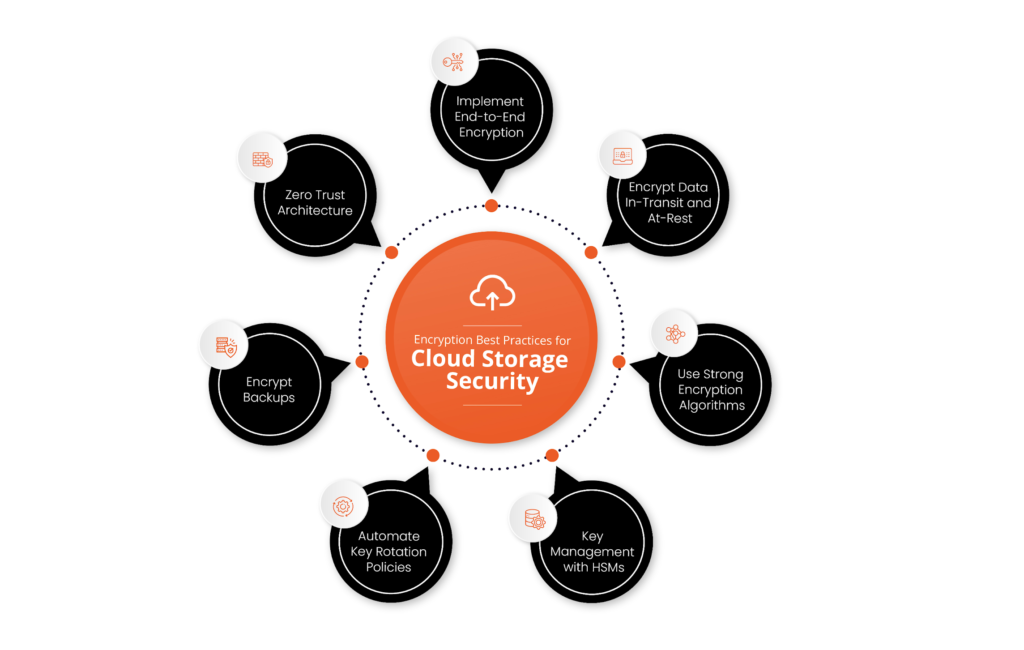
2. Encryption: A Key Security Feature
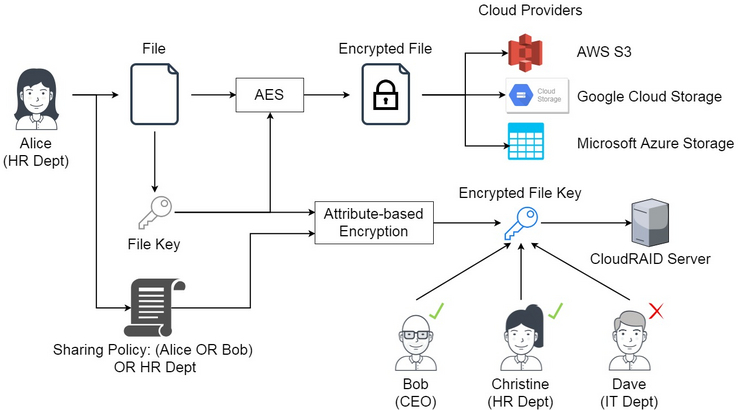
Encryption is one of the most significant security measures used in cloud storage. Data is encrypted both during transmission and at rest. This means that data is scrambled into an unreadable format as it moves between your device and the cloud server, and it remains encrypted while stored. Only users with the proper decryption keys can access the original data, minimizing the chances of it being misused if intercepted. While encryption does not eliminate risks, it significantly reduces the chances of a data breach.
3. Access Control and Authentication Mechanisms
Cloud storage providers implement advanced access control and authentication protocols to safeguard user data. Features like multi-factor authentication (MFA) require users to verify their identity using two or more verification steps, making it challenging for unauthorized users to gain access. Role-based access control (RBAC) is another feature that limits data access based on user roles within an organization, ensuring only authorized personnel can view or manipulate sensitive data.
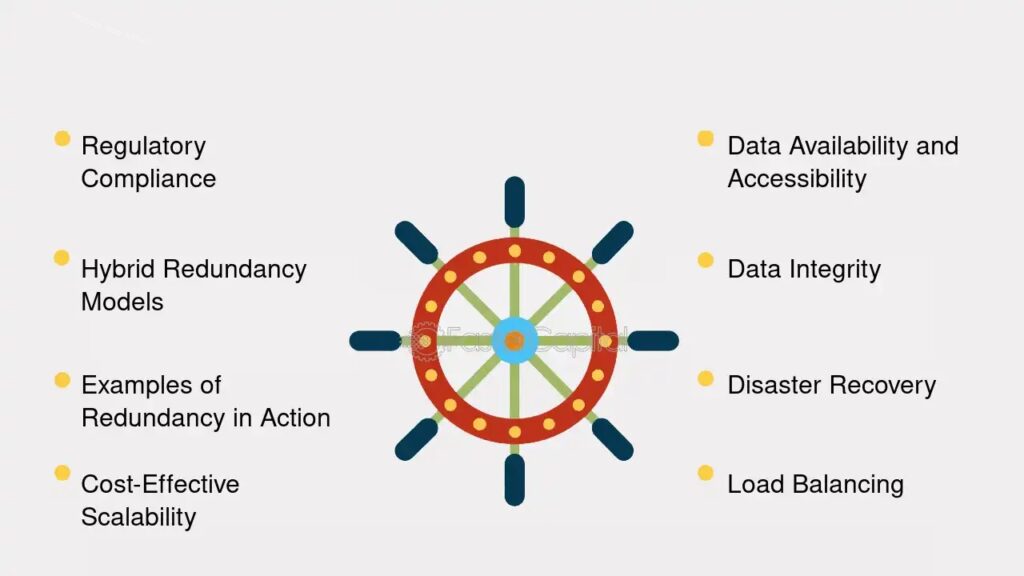
4. Data Redundancy and Backup
One major advantage of cloud storage is data redundancy. Cloud providers typically store multiple copies of data across various locations, protecting it from data loss due to hardware failures, natural disasters, or other unforeseen events. This redundancy ensures that your data remains accessible even if one server or location experiences an issue. Additionally, most cloud providers offer regular backups, so even if data is lost or deleted accidentally, it can be restored from a previous version.
5. Threat Detection and Prevention
Top cloud storage providers utilize sophisticated threat detection tools that monitor data traffic and flag any suspicious activities. Machine learning algorithms analyze patterns to detect potential threats, such as unusual login attempts or data access patterns. Providers also have cybersecurity teams and incident response plans to respond quickly in case of a breach, reducing the potential impact on users.
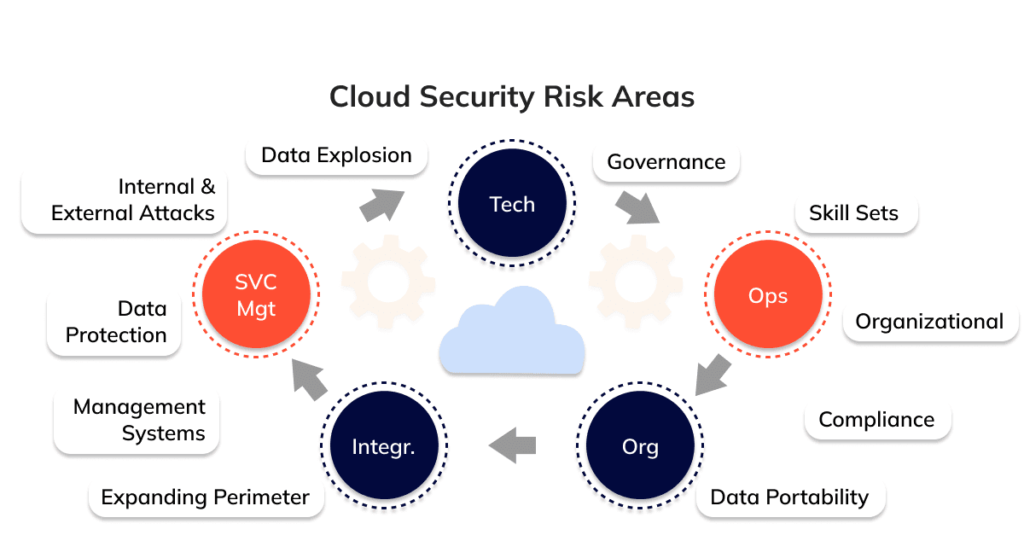
6. Shared Responsibility Model
It’s important to understand the shared responsibility model of cloud security. While cloud providers are responsible for securing the infrastructure (including servers, networks, and physical facilities), users are responsible for securing their data within the cloud. This includes managing permissions, securing credentials, and following cybersecurity best practices. Properly securing your end, such as using strong passwords and enabling MFA, significantly enhances data safety in the cloud.

7. Data Compliance and Privacy Regulations
Reputable cloud providers comply with industry-specific regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO certifications. These standards require providers to follow stringent security and privacy practices, ensuring that they protect user data and respect privacy rights. Compliance with these standards offers users an added layer of confidence, as cloud providers are regularly audited for adherence to these practices.
Are There Risks with Cloud Storage?
While cloud storage is generally secure, no system is entirely risk-free. Cyber threats like data breaches, ransomware, and insider threats still pose potential risks. However, compared to traditional storage methods, the cloud offers significantly more robust security capabilities due to the expertise and resources that providers invest in cybersecurity.
Is Cloud Storage a Safe Option?
Cloud storage can be a safe option for data storage, especially when provided by reputable companies with strong security practices. With encryption, access control, data redundancy, threat detection, and regulatory compliance, cloud storage provides a secure environment for data. However, users must play their part by following cybersecurity best practices and understanding the shared responsibility model.
In an increasingly connected world, cloud storage offers not only safety but also the flexibility and convenience that traditional storage can’t match. When used responsibly, cloud storage can be a reliable and secure way to manage and protect your valuable data in the face of evolving cybersecurity threats.